Subject 1: Non-invasive methods to observe the brain and its activity
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive method to create images of body tissues. Contrary to Computer Tomography or X-rays, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, but a strong magnetic field instead. The magnetic field aligns protons in the tissues’ water molecules in the same direction. Then a radio frequency signal is briefly emitted and disrupts the protons’ alignment with the magnetic field. After the signal is turned off, the protons flip back to their aligned position. During this flip back they send a radio frequency signal which can be detected by the MRI scanner. Protons in different tissues flip back at different speed, allowing the differentiation of these tissues and thus the creation of an image that usually shows them in different gradients of grey (Figure 1).
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is based on MRI and is a method to observe brain activity by measuring the change of the amount of oxygen in the blood and blood flow. Whenever a cell is active it requires glucose as the main source of energy. Along with glucose consumption, also the oxygenation of blood (i.e. the concentration of oxygen in the blood) changes. Since oxygenated blood has different magnetic properties than deoxygenized blood, a similar method as in MRI can be used to detect in which parts of a tissue neurons are active. In the image this activity is usually shown in different colors that are overlaid over a regular MRI image (Figure 2). FMRI measures activity at a spatial resolution of cubic millimetres or less and activity changes in a time window of about 2-3 seconds.
Based on the text above, which of the statements below are true, which are false?
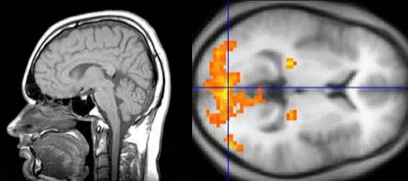
Figure 2: fMRI image (horizontal cut) of the brain showing the strength of neural activity color coded from yellow to red.